Appendices
Disclaimer: The information provided in this appendix is a guide to the legislation related to fertilisers. AIC shall not be responsible for keeping this list up to date or for any errors or omissions. The company participating in FIAS is responsible for ensuring that it is aware of all legislation related to their business. Ensure EU Exit and devolved nation legislation is considered.
Agent (or Broker)
An agent (or broker) facilitates a contract between a buyer and a seller but takes no financial involvement in the transaction except to receive a commission from either buyer or seller or both. If a Body, Person or Company that acts as a principal to the debt incurred in the supply of fertiliser, they are a merchant. If the agent is authorised to agree sales on behalf of a company or enter sales into the system then they must be trained as a sales representative.
Blended fertiliser
A fertiliser obtained by dry mixing of more than one fertiliser, with no chemical reaction.
Business process risk assessment
An assessment for the purposes of FIAS which identifies the hazards, threats and resulting risks related to legal compliance, security, traceability and product safety of all fertiliser operations undertaken by the business.
It is distinct from a Health and Safety Risk Assessment but may follow similar principles.
Caking tendency
The ability for fertiliser granules or prills to form an agglomeration. Mechanisms for caking are numerous and include formation of crystal bridges due to incompatibility or post reactions, moisture content and/or pick up, high fines/dust content and granule deformation.
Company
The organisation certified or seeking certification under FIAS.
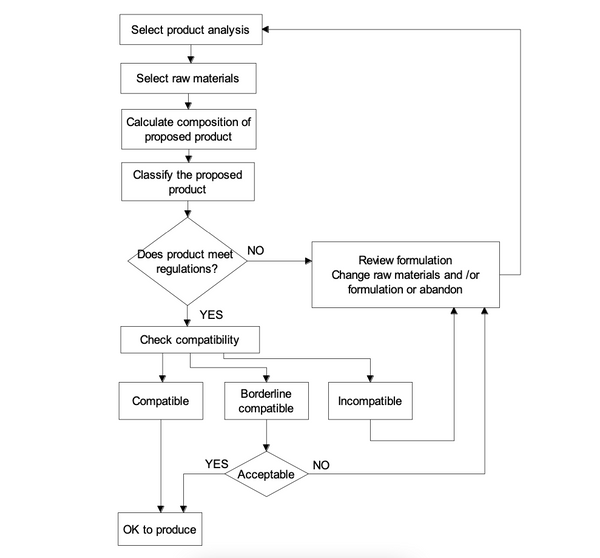
Compatibility
Materials when mixed together are not necessarily compatible with each other; some may produce undesirable effects when mixed with others; in other words, they may not be compatible. These undesirable effects can include chemical reaction(s) and physical effects e.g. stickiness which can cause handling difficulties, moisture migration giving rise to caking tendency. For reasons of safety, it is very important to avoid blending ammonium nitrate or raw materials containing ammonium nitrate with any organic materials.
Detonation Resistance Test (DRT)
A test carried out by a competent laboratory in accordance with Schedule 2 of the Ammonium Nitrate Materials (High Nitrogen Content) Safety Regulations 2003.
Foliar fertiliser
A fertiliser suitable for application to and nutrient uptake by the foliage of a crop.
Manufacturer
The natural or legal person responsible for placing a fertiliser on the market; in particular a producer, a blender, an importer, a packager working for its own account, or any person changing the characteristics of a fertiliser, shall be deemed to be a manufacturer. However, a distributor who does not change the characteristics of the fertiliser shall not be deemed to be a manufacturer.
Merchant
The Body, Person or Company that acts as a principal to the debt incurred in the supply of fertiliser to a customer and does not change the characteristics of the fertiliser. For the purposes of FIAS, companies which pack or repack fertilisers themselves, or engage a contract packer to do so on their behalf fall within the definition of manufacturer.
Micro-nutrients
The elements boron, cobalt, copper, iron, manganese, molybdenum and zinc, essential for plant growth in quantities that are small compared with those of primary and secondary nutrients.
Non-conforming product
Non-conforming materials are those materials which do not meet the characteristics of the intended products at the time of storage or when marketed. They include both off-spec and reject materials, which are defined below. Essentially, they include everything other than marketable specified product.
Off-spec
The definition of “off-spec” given in The Control of Major Accident Hazards (Amendment) Regulations 2005 is as follows:
Material rejected during the manufacturing process and to ammonium nitrate and preparations of ammonium nitrate, straight ammonium nitrate-based fertilisers and ammonium nitrate-based compound/composite fertilisers referred to in Notes 2 and 3, that are being or have been returned from the final user to a manufacturer, temporary storage or reprocessing plant for reworking, recycling or treatment for safe use, because they no longer comply with the specifications of Notes 2 and 3; or
(b) fertilisers which do not fall within Notes 1(a) and 2, because they do not satisfy the detonation resistance test, other than fertilisers which -
-
(i) at the time of delivery to a final user satisfied the detonation resistance test; but
-
(ii) later became degraded or contaminated; and
-
(iii) are temporarily present at the establishment of the final user prior to their return for reworking, recycling or treatment for safe use or to their being applied as fertiliser.
Placing on the market
The supply of fertiliser, whether in return for payment or free of charge, or storage for the purpose of supply. Importation of a fertiliser into the customs territory of the UK shall be deemed to constitute placing on the market.
Product
All fertilisers intended for agriculture, horticulture, forestry, amenity and any other such commercial use, straight or blended.
Product Recall
Product recall is the process required to enable identification and location of non-conforming material or product at all points in the supply chain between producer and end user in order for remedial action to be agreed and implemented by the parties involved.
Raw Material
Ingredient used in the production of fertiliser intended for agriculture, horticulture, forestry, amenity and any other such commercial use.
Reject
Reject materials are those non-conforming materials which are out of specification, or which have deteriorated during storage and/or handling to such an extent that they can be considered potentially hazardous. They cannot be sold as fertiliser products and may require treatment to render them safe. Examples include those which contain more than the maximum permitted level of combustible material; those which have physically degraded into fines and could reasonably be expected to fail the Detonation Resistance Test; product grossly contaminated with reactive substances.
Relevant Ammonium Nitrate
The definition given in the Ammonium Nitrate Materials (High Nitrogen Content) Safety Regulations 2003 is:
Ammonium nitrate in solid form, where its nitrogen content is more than 28% of its weight,
material in solid form, comprising a mixture of components, one of which is ammonium nitrate, in circumstances where the nitrogen content derived from ammonium nitrate is more than 28% of the material by weight, and where the material has a total weight of five hundred kilogrammes or more, but does not include material which is a classified explosive.
Relevant Ammonium Nitrate Mixtures
The Dangerous Substances (Notification And Marking Of Sites) (NAMOS) Regulations define ‘relevant ammonium nitrate mixtures’ as ammonium nitrate and mixtures containing ammonium nitrate, where the nitrogen content exceeds 15.75% of the mixture by weight. This definition was transferred from the NIHHS Regulations.
Resistance to detonation
The ability of a fertiliser to resist detonation determined by the Detonation Resistance Test.
Self-sustaining decomposition
A fertiliser capable of self-sustaining decomposition is defined as one in which decomposition initiated in a localised area will spread through the mass after removal of the initiating heat source. This type of fertiliser is commonly known as a “cigar burner”.
Source of Supply
The place from which materials are purchased.
Storage
The provision of facilities for the holding of stocks of fertiliser such as warehouse buildings, outside areas including port quaysides, on either an ongoing, temporary or in-transit basis, together with management of personnel employed and the operation of any equipment used, for the handling of such fertiliser.
Straight fertiliser
A nitrogenous, phosphoric or potassic fertiliser having a declarable content of only one of these primary nutrients.
Supplier
The company that sells fertiliser within the scope of FIAS
Suspension fertiliser
A concentrated suspension of finely divided nutrients in a supersaturated nutrient solution, stabilised using a clay or polymer based gelling agent, allowing tailor-made ratios of N, P, K, Mg, Na, S, B, Mn, Zn, Cu, Mo and Se plus nitrification inhibitors and phosphate enhancers to be uniformly applied to the soil by spray application
Thermal cycling
A thermal cycle is the application of heat to a closed sample of ammonium nitrate to a temperature of 50OC followed by cooling to 25OC. The combination of successive phases at 50OC and 25OC forms one thermal cycle.
Traceability
The ability to track and follow a material or product through all stages of sourcing, production, storage, sales and distribution to end user.
The following is a list of the records identified within the text of FIAS and which must be kept.
|
Clause No |
Record Required |
|---|---|
|
Policy statement |
|
|
Management review |
|
| Records of communication of staff responsibilities | |
|
Training and competence records |
|
| G6.3 |
Security screening of staff |
|
Notification/approvals for products held on site. |
|
|
Business process risk assessment records - team members, risks associated with the products, process descriptions, hazard and risk assessments, controls and action plans |
|
|
Business process assessment review |
|
| G13.1 | Supplier approval |
|
Purchase specifications and records |
|
|
Contracted services – FIAS certification confirmation |
|
|
Non-FIAS Contractor or merchant customer initial audit and inspection assessments, reports and authorisations. |
|
|
Non-FIAS Contractor or merchant customer annual audit and inspection assessments, reports and management review record. |
|
|
Internal audit reports and follow-up information |
|
| G19.1 | Document control records |
|
Incident management procedure and review |
|
|
Notification of suspicious or unusual activity to enforcement agencies; actions taken |
|
|
Traceability records |
|
| G21.6 | Verification of product recall system in management review |
|
Complaints and actions taken |
|
| G24.1 | Purchase contracts for products sourced from overseas |
|
Notification to authorities of AN import |
|
| G24.2 | Compliance of fertiliser imports to specification and legislation |
|
DRT certificate/product transaction records |
|
| MP1.1 | Management of new product development |
|
Product inspection/test records |
|
| MP6.1 | Non-conforming product records |
|
Contingency plan for DRT failed AN |
|
| MP7.1 | Equipment calibration, Calibration failure investigation |
|
Fire detection system and firefighting equipment maintenance |
|
| S4.1 | Notification and signage for products held |
|
Product changeover cleaning record |
|
|
Verification of incoming material |
|
|
Appointment of DGSA, certificate and annual report |
|
|
Signature and name of employee Agreement of other verifiable means |
|
|
Checks of vehicle/driver legal compliance |
|
| S7.3 | Name/Signature of driver |
|
Customers and product sales checks |
|
| M1.2 | Non account holding customer details |
|
Customer and sales records |
|
| M1.6 | Evaluation of suspicious request to purchase products |
|
Customer requirement records |
|
| M2.1 | Training of sales representatives |
|
Agent responsibilities |
|
| Approval of hauliers | |
|
Verification of compliance |
|
|
Instructions received from clients Bona fide client checks |
|
|
Instructions passed to drivers |
|
| Current operator's licence | |
|
Appointment of DGSA and certificate |
|
| T7.2 | Damage or loss reporting |
|
Security measures taken when parked/ unattended |
|
| T9.1 | Approval of diversion of deliveries |
|
Discrepancies on delivery |
|
| T9.3 | Proof of delivery/ Risk assessment |
|
Proof of delivery/ Risk assessment for bulk solid or liquid fertilisers |
|
Agricultural Industries Confederation (AIC) Tel: 01733 385230 www.agindustries.org.uk |
Logistics UK |
|
Anti-Terrorist Reporting |
Health and Safety Executive (HSE) |
|
National Counter Terrorism Security Office (NaCTSO) |
Home Office |
|
BASIS / FACTS |
International Fertiliser Society |
|
Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs (Defra) Tel: 03000 200 301 |
Kiwa Agri-Food |
|
Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy (BEIS) Tel: 020 7215 5000 |
National Farmers Union (NFU) |
|
Department for Transport (DfT) |
National Farmers Union Scotland (NFUS) |
|
Driver and Vehicle Standards Agency |
Red Tractor Farm Assurance |
|
Environment Agency |
Road Haulage Association (RHA) |
|
Fertilizers Europe |
United Kingdom Accreditation Service (UKAS) |
-
Under the Dangerous Substances (Notification And Marking Of Sites) (NAMOS) Regulations 1990, as amended on 6th April 2013, sites which store certain fertilisers have a requirement to notify the relevant authorities and display warning signage at the site entrances.
-
Sites which hold 25 tonnes of material classified as being ‘Dangerous Substances’ are required to notify both the HSE and local Fire and Rescue Service. This includes all fertilisers which display the hazardous classification symbol for 5.1 oxidising substances under the Carriage of Dangerous Goods regulations (ADR). (This will include Ammonium Nitrate based products).
-
Sites which hold 25 tonnes of material classified as being ‘Dangerous Substances’ are required to place a ‘Dangerous Substance’ warning symbol at all access points to the site.
-
A person in control of a site which holds a total quantity of 150 tonnes or more of ‘relevant ammonium nitrate mixtures’ (see Appendix 3 definitions) are required to notify the Fire and Rescue Service for the area in which the site is located. (There is no requirement to notify the HSE).
A typical ratio would be 25.5.5 which equates to 25% N, 5% P and 5% K. In this example the Nitrogen would contain both Nitric Nitrogen (N) 12.5%, and Ammoniacal Nitrogen (N) 12.5%, thus making the total Nitrogen (N) content 25%.
1. The Control of Explosives Precursors and Poisons Regulations 2023 (CEPPR), as part of the Poisons Act 1972 apply to suppliers and sellers (producers, distributors and merchants) of regulated and reportable substances at all stages of the supply chain and are concerned with the ownership of the goods, not custody.
Reference: FIAS Standard clause: G9.1
Regulated and Reportable substances are listed in the Poisons Act 1972, Schedule 1A.
Reportable substances may be on sale to the public and carry an obligation to report suspicious or attempted transactions.
Regulated substances are those whose sales are restricted to businesses and members of the public who hold a Home Office Explosives Precursors and Poisons (EPP) licence. Listed substances at a concentration below the stated regulated threshold such as below 16% N from AN), are still considered reportable substances.
The substances may be present alone or mixed with other materials.
For example, fertilisers containing 16% or above nitrogen (N) from ammonium nitrate (AN) are regulated products.
2. Under the CEPPR 2023, supply of regulated fertiliser substances to a business customer is not permitted unless the following are completed by the supplier:
a) Supply chain notification: notify the customer in writing if the fertiliser substance to be supplied is regulated or reportable
b) Customer verification: collect, verify and record all of the following information from the customer:
i) name and address of business customer OR
ii) name of an individual authorised on behalf of the business customer
iii) photographic identification of the business customer or the authorised individual
iv) statement of the nature of business customer’s trade, business or profession
v) VAT registration number if available
Photographic ID must show details of the name of the person. Passport, driving licence, trade card, travel pass are all examples of acceptable formats.
Only one photographic ID is required to allow any member of that business to make a purchase.
Reference: FIAS Standard clause: M1.1,1.2
c) Records, retention and review
The customer information held must be no older than 18 months and be reverified every 18 months. Reference: FIAS Standard clause: G19.3
d) Training staff. Those involved in the sales of fertilisers must be trained in:
- which products are regulated or reportable
- requesting relevant information and identification from customers
- recognising suspicious behaviour
- reporting suspicious activity and transactions
- obligations and the potential offences which apply
Training materials are available from the Protect UK website: https://www.protectuk.police.uk/advice-and-guidance/awareness/poisons-act-1972-selling-chemicals-responsibly
Reference: FIAS Standard clause: G6, M2.1
e) Suspicious Activity Reporting – this must be completed within 24 hours of becoming suspicious, preferably via the online portal, or if not possible, via the national contact point on 0800 789321.
Reference: FIAS. Standard clause: M1.6, M2.2
Additional information:
Web link: CEPPR https://www.legislation.gov.uk/uksi/2023/63/contents
Official Guidance: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/supplying-explosives-precursors/supplying-explosives-precursors-and-poison
Suspicious activity reporting online: https://report-suspicious-chemical-activity.dsa.homeoffice.gov.uk/login
AIC Guidance, FAQs:
https://www.agindustries.org.uk/resource/explosives-precursors.html
CEPPR and General Data Protection Regulations (GDPR)
The requirement within CEPPR to collect and hold information about customers means that additional legislation applies under UK GDPR. The CEPPR 2023 provides a legal obligation (lawful basis) to collect data and retain it for 18 months. Collection and retention of this data should be communicated to customers in the supplier’s privacy notices.
Data is to be re-verified after 18 months and if no longer active, should be deleted.
Each supplier has a responsibility to keep the data safe and secure so it can be made available if it is needed within the 18-month period. If data records are not suitably secured, are stolen, mislaid or damaged in the case of paper records, this counts as a breach of data protection.
Further guidance for businesses on GDPR is available from the website of the UK Regulator, the Information Commissioner’s Office: https://ico.org.uk/for-organisations/uk-gdpr-guidance-and-resources/